Introduction
The assessment of body composition and skeletal muscle morphofunctionality has gained importance in recent years due to its close relationship in the development and morbidity and mortality of different highly prevalent pathologies in our health system. Its assessment offers a more complete view of the individual’s health status and its knowledge allows adjusting interventions or medical treatments.
There are different techniques for this, with bioelectrical impedance or bioimpedance (BIA) being the most widely used technique in recent decades due to its availability and ease of use. However, it does not offer a complete view of the individual’s muscle morpho-functionality and has limitations in certain pathologies.
For this reason, and as a complement to bioimpedance assessment, nutritional ultrasound is increasingly used, which studies both muscle and abdominal fat, and certain functional tests such as the short physical performance battery or SPPB.
The Unit also has dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry equipment or densitometer (DEXA), a technique considered the gold standard in assessing body composition that estimates the different body compartments with high precision.
The muscle composition and function parameters obtained by the different tests allow different diagnoses to be made: malnutrition, obesity, sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity, frailty and osteoporosis/osteopenia.
Services
From the following techniques:
- Whole body densitometry for assessment of body composition:
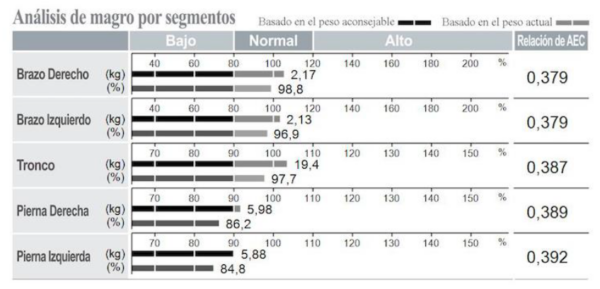
It is a tricompartmental technique that provides data on fat mass, lean mass (total and appendicular) and bone mass both at the level of the whole body and by body segments (right arm, left arm, trunk, right leg and left leg).
In addition, thanks to a built-in software, it allows to assess the visceral fat tissue.
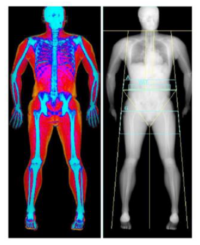
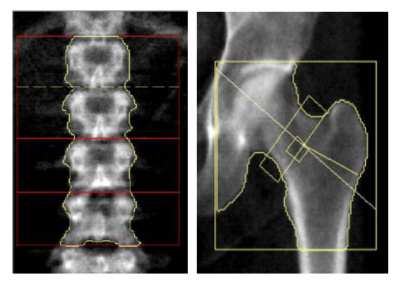
- Bone densitometry of two zones to assess bone mineral density: : Bone mineral density and the T-score and Z-score are assessed both at the level of the lumbar spine and at the level of the hip for the diagnosis of osteoporosis and risk of fracture.
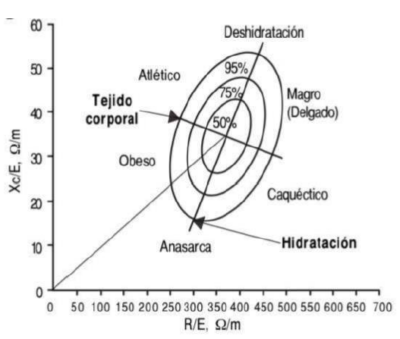
- Multi-frequency bioimpedance: Estimates with high precision the different body compartments (fat mass, fat-free mass, muscle mass and body water) in terms of kg, percentages and body indices (kg/m2) and provides cellular health parameters such as are the phase angle and the body cell mass index. Thanks to the range of frequencies it uses, multi-frequency BIA allows the individual to assess with good precision the body fluids at the extra and intracellular level.
In addition, by using 8 tactile point electrodes, it is considered a segmental technique and allows the assessment of body composition both at level of the whole body as well as of the different body segments (right arm, left arm, trunk, right leg and left leg).
- Monofrequency bioimpedance:It is a portable IAB that is used with the individual in the supine position, useful in hospitalized patients. It estimates with high precision the different body compartments (fat mass, fat-free mass, muscle mass and body water) in terms of kg, percentages and body indices (kg/m2) and provides cell health parameters such as phase angle and body cell mass index.
It does not allow intracellular fluids to be assessed with such good precision since it uses a single frequency and it does not offer segmental study either since it only uses 4 electrodes.
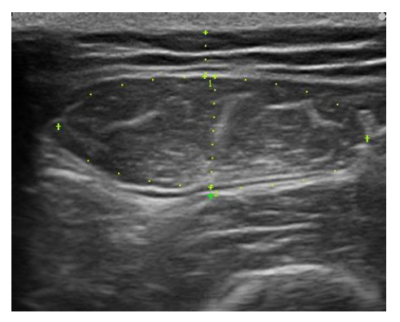
- Muscular and adipose tissue ultrasound (nutritional ultrasound): The ultrasound known as nutritional ultrasound assesses both the morphofunctionality of the skeletal muscle at the level of the rectus femoris and the adipose tissue (subcutaneous and preperitoneal) at the abdominal level.
- Functional tests:
– The SPPB (Short Physical Performance Battery) consists of three functional tests: the balance test, the gait speed test, and the chair rise test. It allows assessing the patient’s functionality and classifying it as dependent, frail, pre-frail or independent.
– Timed Up and Go: allows to assess the risk of falls in the elderly population.
– Dynamometry: using a hydraulic dynamometer, the grip strength of the hand is measured to assess muscle strength.
Services:
- Diagnosis of osteoporosis by bone densitometry of the hip and spine.
- Diagnosis of sarcopenia by dynamometry, functional test and whole body densitometry as a technique for assessing muscle mass.
- Diagnosis of sarcopenia by dynamometry, functional test and multifrequency/monofrequency bioimpedance as a technique for assessing muscle mass.
- Estimation of morphofunctional parameters of skeletal muscle by nutritional ultrasound..
- Assessment of body composition and comprehensive muscle morphofunctionality (whole body densitometry, bioimpedance, nutritional ultrasound and functional tests).
Equipment


Hologic Horizon Wi Model Densitometer
Multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance (INBODY 770)

Akern NutriLab® single-frequency bioelectrical impedance model
Mindray Z50 model ultrasound machine

Jamar® Hydraulic Dynamometer
Rates
Rate A: Users of the institution itself.
Rate B: National public or private non-profit institutions and organizations associated with public centres.
Rate C: Institutions and private organizations.
| Rate A | Rate B | Rate C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis of osteoporosis | €60 | €80 | €100 |
| Diagnosis of sarcopenia by DEXA | €72 | €96 | €120 |
| Diagnosis of sarcopenia by BIA | €30 | €40 | €50 |
| Nutritional ultrasound | €54 | €72 | €90 |
| Comprehensive body composition assessment | €132 | €176 | €220 |
Responsible
PhD. Miguel Civera Andrés
Team
Blanca Alabadí Pardiñes
Sandra Amores Alandí
Ning Yun Wu Xiong
Contact
balabadi@incliva.es
689287472 – 961973861
Hospital Clínico Universitario de Valencia
Blasco Ibáñez Avenue No. 17
Endocrinology Laboratory
Pavilion A, 2nd Floor
46010 Valencia
Business hours
Monday to Thursday from 4:00 p.m. to 7:00 p.m.
